Blockchain Technology: Examine the role of blockchain in various industries and its potential for disrupting traditional systems
This article highlights 15 such applications, Blockchain Technology displaying how Blockchain Technology can rename secure online projecting a voting form, defend balloter honors, and lift greater part rule venture higher than at any time in recent memory.
Importance of blockchain and its fundamental features:
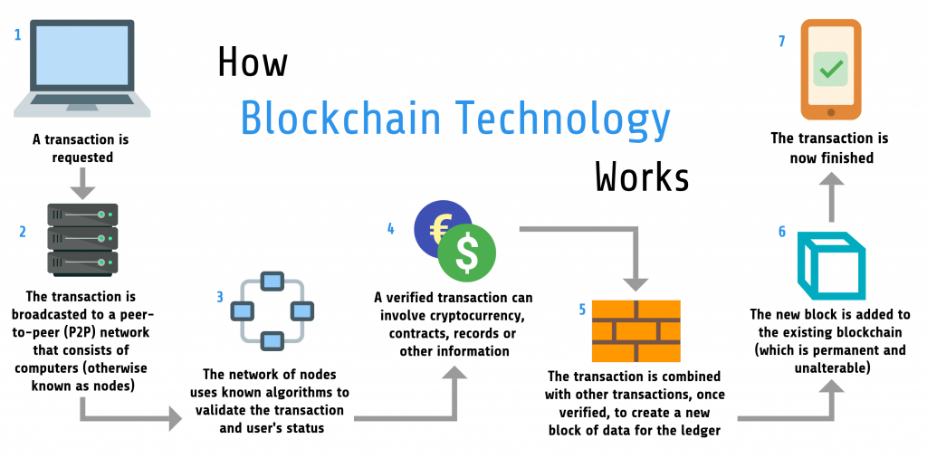
Blockchain Technology is a decentralized and conveyed electronic record development that records trades in a protected and clear manner. it fills in as a successive chain of blocks, each containing a lot of trades, which are associated together using cryptographic hashes.
The middle features of blockchain include:
Decentralization
Immutability
Straightforwardness
Security
Arrangement instrument
Quick arrangements
Cryptographic hashing
Public and private keys
Shared network
Data consistency decentralization:
As opposed to regular concentrated systems, Blockchain Technology deals with a decentralized association of computers (centers), where each center point stores a copy of the entire Blockchain Technology. this discards the prerequisite for a central ability to supervise and really take a look at trades.
Changelessness:
At the point when a trade is recorded on the blockchain, it is unbelievably difficult to change. each block contains a unique cryptographic hash of the past block’s data, making a chain of interlinked blocks that ought to be changed simultaneously to play with a singular trade.
Straightforwardness:
All individuals in a blockchain association can access and view the entire trade history. this straightforwardness further develops liability and trust, as any unapproved changes can be easily distinguished.
Security:
Blockchain Technology uses cryptographic estimations to get trades and assurance the genuineness of the data. trades are checked by understanding parts, making it significantly impenetrable to deception and unapproved access.
Arrangement part:
Blockchain networks use arrangement parts, similar to check of work (pow) or proof of stake (pos), to support and choose the state of the record. understanding ensures that all individuals have a solid viewpoint on the data.
Wise arrangements:
Wise arrangements are self-executing contracts with predefined rules encoded clearly into the blockchain. they normally execute when express conditions are met, discarding the necessity for center individuals and redesigning computerization.
Cryptographic hashing:
Trades and data inside blocks are gotten using cryptographic hashing computations. these computations produce unique fixed-size yields (hashes) considering the data, making it practically challenging to dismantle the main data from the hash.
Public and secret keys:
Individuals in a blockchain network have sets of cryptographic keys public key for recognizing evidence and a private key for secure check. trades are embraced with private keys and affirmed with related public keys.
Shared network:
Blockchain relies upon a common association design, where each center examines directly with others. this diminishes reliance on a lone central component and redesigns network flexibility.
data consistency:
All individuals approach comparative data, ensuring that changes are settled upon through arrangement. this consistency disposes of the prerequisite for splitting the difference between different social occasions’ records.
These key features all things considered make blockchain a tricky development with applications going from secure financial trades to store network the chiefs, and as shown earlier, regardless, for changing how we approach secure electronic projecting a voting form.
Decentralized organization:
Blockchain enables the creation of a decentralized vote-based structure, diminishing the effect of concentrated trained professionals and restricting control.
Further developed security:
utilizing cryptographic techniques, blockchain shields against cyberattacks and unapproved permission to the vote-based system.
Steady results:
Blockchain’s second endorsement and recording of votes consider fast vote counting and result dissipating.
Accessibility:
Blockchain-engaged online projecting a voting form takes exceptional consideration of people with versatility restrictions, allowing them to project a voting form from a distance.
Cross-line projecting a voting form
Blockchain works with ruling for occupants abroad, ensuring their help in open choices from any side of the world.
Straightforwardness and obligation:
spectators can screen the entire popularity-based connection, taking into account administrators answerable for staying aware of respectability.
Diminished costs:
Completing blockchain diminishes costs related to standard popularity-based strategies, potentially supporting optional efficiency.
Adaptability to projecting a voting form structures:
Blockchain’s flexibility licenses it to conform to various majority rule structures, obliging arranged political choice plans all over the planet.
Assurance concerns:
Changing the straightforwardness of blockchain with voter assurance is dire to ensure that solitary popularity-based choices stay arranged.
Straightforward connection points:
Arranging regular and straightforward points of interaction for residents of all mechanical establishments is central to preventing voter preclusion.
See moreover the intersection point of blockchain and man-made knowledge – the accompanying backcountry 3 weeks earlier assurance from new development
Beating uncertainty and security from taking on new development, especially among additional carefully prepared ages, is a deterrent in executing blockchain-based projecting a voting form.
Centralization possibilities:
While blockchain is decentralized, foolish execution could incite centralization of power inside the genuine development.
Shortcomings and security bets:
No matter what its power, blockchain isn’t invulnerable to all security risks, requiring constant undertakings to perceive and address shortcomings.
Legal and regulatory troubles:
Changing existing legal designs to oblige blockchain-based projecting voting form systems requires investigating complex regulatory scenes.
trust building:
Gaining public trust in the security and uprightness of blockchain-based projecting voting form systems is earnest for their expansive gathering.
Watching out for these troubles and thoughts will be basic in understanding the most extreme limit of blockchain for secure online projecting a voting form and ensuring its viable coordination into larger part rule processes.
Conclusion:
The potential purposes of blockchain for secure online projecting a polling form offer a short investigation of a future where a larger part of controls government is supported by development.
The straightforwardness, security, and receptiveness of blockchain.

